The area of the smallest equilateral triangle with one vertex on each of the sides of the right triangle with side lengths $2\sqrt{3}$, $5$, and $\sqrt{37}$ as shown, is $\dfrac{m\sqrt{p}}{n}$, where $m$, $n$, and $p$ are positive integers, and $m$, $n$, and $p$ are relative prime, and $p$ is not divisible by the square of any prime. Find $m+n+p$.
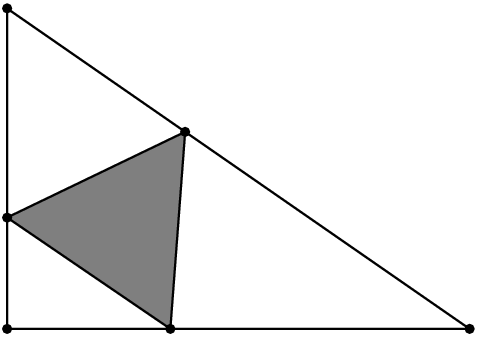
Solution: Let the coordinates of the triangle vertices as $O=(0,0)$, $X=(5,0)$, $Y=(0,2\sqrt{3})$. And the coordinates of the equilateral triangle on the $x$-axis and $y$-axis as $A=(a,0)$ and $B=(0,b)$. Then the coordinate of the third vertex $C$ of the equilateral triangle can be calculated by rotating line $AB$ $60^\circ$ clockwise around $A$, which is $$(a+(-a\cdot\cos(60^\circ)+b\cdot\sin(60^\circ)), b\cdot\cos(60^\circ)-(-a\cdot\sin(60^\circ)))$$
Simplifying the above, we have $$C=(\dfrac{a+b\sqrt{3}}{2},\dfrac{a\sqrt{3}+b}{2})$$
As $C$ is on the line of $XY$, which is $$\dfrac{x}{5}+\dfrac{y}{2\sqrt{3}}=1$$ We have $$\dfrac{\dfrac{a+b\sqrt{3}}{2}}{5}+\dfrac{\dfrac{a\sqrt{3}+b}{2}}{2\sqrt{3}}=1$$
Simplifying the above, we have $$a=\dfrac{60-11\sqrt{3}b}{21}$$
The area of the equilateral $\triangle{ABC}$ is $$\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}\overline{AB}^2=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}(a^2+b^2)$$
$$a^2+b^2=(\dfrac{60-11\sqrt{3}b}{21})^2+b^2=\dfrac{3600-1320\sqrt{3}b+363b^2}{441}+b^2$$ $$=\dfrac{3600-1320\sqrt{3}b+804b^2}{441}$$
Since the minimum value of $f(x)=Ax^2+Bx+C$ is $C-\dfrac{B^2}{4A}$, when $A>0$, the minimum value of $a^2+b^2$ is $$\dfrac{3600-\dfrac{{1320\sqrt{3}}^2}{4\cdot 804}}{441}=\dfrac{300}{67}$$
Therefore the minimum area of the $\triangle{ABC}$ is $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}\cdot\dfrac{300}{67}=\dfrac{75\sqrt{3}}{67}$. Therefore the answer is $75+67+3=\boxed{145}$.
